lv apical aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm | Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo lv apical aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending .
Everyone is always looking for those Patek Philippes, Rolexs, APs, Richard Milles, and other luxury watch brands all over social media. But not only are these watches difficult to get at retail, they are very expensive. Because of that, we thought we’d look at more affordable alternatives to some of the most popular watches on the market.
0 · pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo
1 · pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm
2 · pseudoaneurysm risk factors
3 · left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm
4 · Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo
5 · Lv aneurysm post mi
6 · Lv aneurysm on echo
7 · Lv aneurysm anticoagulation
3. Reply. monki_huhu. • 3 yr. ago. Try this - Geparlys Yes I Am the King - Le Parfum. Highly rated BDC dupe by lots of people. 2. Reply. myrainyday. • 3 yr. ago. I happen to have Cuba Shadow by fragluxe, which is very similar to Bleu De Chanel. Offers a few hours of longevity, sillage is very low.
Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the . Left ventricular false aneurysm is a rare complication of myocardial rupture contained by non-myocardial tissue. The most common cause of a false aneurysm is a transmural myocardial infarction, but it can also .
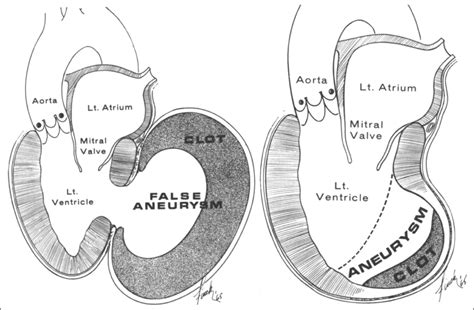
A true aneurysmal sac contains an endocardium, epicardium, and thinned fibrous tissue (scar) which is a remnant of the left ventricular muscle, while a pseudoaneurysm sac .The left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) corresponds to a scar area in the form of a thin-pocket shape communicating with the rest of the LV by a wide necked losing its contractile function due to . Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography showed an apical left ventricular (LV) discontinuity, suggestive of a pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (Figure A, arrows). A . A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending .
A ventricular aneurysm may be a: True ventricular aneurysm: Damage to the heart wall (usually from a heart attack) weakens a section of the ventricle. A blood-filled sac may .
This article illustrates that physicians should be vigilant for atypical presentations of left ventricular pseudoaneurysm, and a high index of suspicion should be maintained for this .
A postmyocardial infarction left ventricular pseudoaneurysm occurs when a rupture of the ventricular free wall is contained by overlying, adherent pericardium. A postinfarction .Abstract. Free wall rupture of the left ventricle (LV) is a rare but life-threatening complication of acute myocardial infaction. Very rarely such rupture may be contained by the adhering pericardium creating a pseudoaneurysm. This condition warrants for an emergency surgery. Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the diagnosis and management of patients with aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms caused by MI.
Left ventricular false aneurysm is a rare complication of myocardial rupture contained by non-myocardial tissue. The most common cause of a false aneurysm is a transmural myocardial infarction, but it can also develop following cardiac surgery, endocarditis, or trauma. A true aneurysmal sac contains an endocardium, epicardium, and thinned fibrous tissue (scar) which is a remnant of the left ventricular muscle, while a pseudoaneurysm sac represents a pericardium that contains a ruptured left ventricle 5.
The left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) corresponds to a scar area in the form of a thin-pocket shape communicating with the rest of the LV by a wide necked losing its contractile function due to transmural necrosis.
Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography showed an apical left ventricular (LV) discontinuity, suggestive of a pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (Figure A, arrows). A minimal pericardial effusion was present. Doppler showed flow passage from the left ventricle into an echo-free space. A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending artery .
A ventricular aneurysm may be a: True ventricular aneurysm: Damage to the heart wall (usually from a heart attack) weakens a section of the ventricle. A blood-filled sac may form in the weakened area. False ventricular aneurysm (pseudoaneurysm): Damage to the ventricular wall allows blood to collect in the pericardium. This article illustrates that physicians should be vigilant for atypical presentations of left ventricular pseudoaneurysm, and a high index of suspicion should be maintained for this stealth killer while performing appropriate diagnostic imaging.
A postmyocardial infarction left ventricular pseudoaneurysm occurs when a rupture of the ventricular free wall is contained by overlying, adherent pericardium. A postinfarction aneurysm, in contrast, is caused by scar formation resulting in thinning of the myocardium.Abstract. Free wall rupture of the left ventricle (LV) is a rare but life-threatening complication of acute myocardial infaction. Very rarely such rupture may be contained by the adhering pericardium creating a pseudoaneurysm. This condition warrants for an emergency surgery.
pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo
Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the diagnosis and management of patients with aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms caused by MI. Left ventricular false aneurysm is a rare complication of myocardial rupture contained by non-myocardial tissue. The most common cause of a false aneurysm is a transmural myocardial infarction, but it can also develop following cardiac surgery, endocarditis, or trauma. A true aneurysmal sac contains an endocardium, epicardium, and thinned fibrous tissue (scar) which is a remnant of the left ventricular muscle, while a pseudoaneurysm sac represents a pericardium that contains a ruptured left ventricle 5.The left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) corresponds to a scar area in the form of a thin-pocket shape communicating with the rest of the LV by a wide necked losing its contractile function due to transmural necrosis.
Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography showed an apical left ventricular (LV) discontinuity, suggestive of a pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (Figure A, arrows). A minimal pericardial effusion was present. Doppler showed flow passage from the left ventricle into an echo-free space. A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending artery . A ventricular aneurysm may be a: True ventricular aneurysm: Damage to the heart wall (usually from a heart attack) weakens a section of the ventricle. A blood-filled sac may form in the weakened area. False ventricular aneurysm (pseudoaneurysm): Damage to the ventricular wall allows blood to collect in the pericardium. This article illustrates that physicians should be vigilant for atypical presentations of left ventricular pseudoaneurysm, and a high index of suspicion should be maintained for this stealth killer while performing appropriate diagnostic imaging.
givenchy camouflage passport holder
givenchy capelet dress

Victorinox Maverick. #3. Seiko SRP Diver. #2. Tissot Seastar. #1. Hamilton Khaki Scuba. Omega Seamaster Alternatives – FAQ. Omega Seamaster .
lv apical aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm|Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo