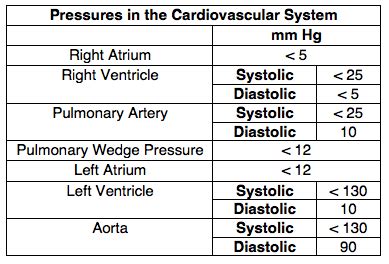
lv pressure chart | normal lv filling pressure lv pressure chart Normal circulation with representative right and left cardiac pressures (in mm Hg) Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. Atrial pressures are mean pressures. Rolex Datejust 41 (Ref. 126301-0008) Please Call for Pricing. MORE INFO.
0 · normal lv pressures
1 · normal lv pressure range
2 · normal lv filling pressure
3 · normal lv end diastolic pressure
4 · normal blood pressure chart
5 · lvedp blood pressure chart
6 · lv pressure sensor
7 · lv end diastolic pressure
News’ exclusive first look at Secrets of the Hells Angels, the detailed audio diaries of Margo Compton—who was murdered in 1977—are broadcast for the first time .
rolex gmt master 2 watchfinder
Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Adapted from Fowler NO: Cardiac Diagnosis and Treatment, ed 3. Philadelphia, JB Lippincott, 1980, p. 11.Normal circulation with representative right and left cardiac pressures (in mm Hg) Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. Atrial pressures are mean pressures.
Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2, maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). ∗∗ In the absence of other .Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of . Overview. Normal intracardiac pressures (see chart above) Pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP) an approximation of left atrial pressure and left ventricular diastolic pressure. measured with Swan-Ganz catheter. in mitral . Use our blood pressure chart to learn what your blood pressure levels and numbers mean, including normal blood pressure and the difference between systolic and .
rolex gmt master 2 matte black
Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Type of Pressure. Average (mm Hg) Range (mm Hg) Right atrium. 3. 0–8. Right ventricle.To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase . Maximal instantaneous gradient is the maximum pressure gradient between the aorta (purple) and left ventricle (yellow) at a single point in time. Peak-to-peak gradient is the . Confused by blood pressure numbers? Learn more about normal ranges for systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings in this in depth explanation with chart from MD.
Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Adapted from Fowler NO: Cardiac Diagnosis and Treatment, ed 3. Philadelphia, JB Lippincott, 1980, p. 11.Normal circulation with representative right and left cardiac pressures (in mm Hg) Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. Atrial pressures are mean pressures.
Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2, maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). ∗∗ In the absence of other etiologies of LV and LA dilatation and acute MR.Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Overview. Normal intracardiac pressures (see chart above) Pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP) an approximation of left atrial pressure and left ventricular diastolic pressure. measured with Swan-Ganz catheter. in mitral stenosis, PWP > left ventricular diastolic pressure. Use our blood pressure chart to learn what your blood pressure levels and numbers mean, including normal blood pressure and the difference between systolic and diastolic.
Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Type of Pressure. Average (mm Hg) Range (mm Hg) Right atrium. 3. 0–8. Right ventricle.To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase b, systole), ejection (phase c, systole), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase d, diastole).
Maximal instantaneous gradient is the maximum pressure gradient between the aorta (purple) and left ventricle (yellow) at a single point in time. Peak-to-peak gradient is the absolute difference between peak aortic systolic pressure .
Confused by blood pressure numbers? Learn more about normal ranges for systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings in this in depth explanation with chart from MD.Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Adapted from Fowler NO: Cardiac Diagnosis and Treatment, ed 3. Philadelphia, JB Lippincott, 1980, p. 11.Normal circulation with representative right and left cardiac pressures (in mm Hg) Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. Atrial pressures are mean pressures. Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2, maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2, maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). ∗∗ In the absence of other etiologies of LV and LA dilatation and acute MR.
Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Overview. Normal intracardiac pressures (see chart above) Pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP) an approximation of left atrial pressure and left ventricular diastolic pressure. measured with Swan-Ganz catheter. in mitral stenosis, PWP > left ventricular diastolic pressure. Use our blood pressure chart to learn what your blood pressure levels and numbers mean, including normal blood pressure and the difference between systolic and diastolic.
Normal Pressures in the Heart and Great Vessels. Type of Pressure. Average (mm Hg) Range (mm Hg) Right atrium. 3. 0–8. Right ventricle.To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase b, systole), ejection (phase c, systole), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase d, diastole).
Maximal instantaneous gradient is the maximum pressure gradient between the aorta (purple) and left ventricle (yellow) at a single point in time. Peak-to-peak gradient is the absolute difference between peak aortic systolic pressure .
normal lv pressures
normal lv pressure range
normal lv filling pressure
Oversized Sneaker. $ 790. Discover men's shoes at Alexander McQueen, featuring luxury hybrid, oversized, sprint runner, tread slick & punk footwear. Enjoy free express shipping.
lv pressure chart|normal lv filling pressure